
15 May Tethering: Network Access from Anywhere
Staying connected to the internet is crucial, especially for organizations that rely on remote access to computing resources and data.
 What is Tethering?
What is Tethering?
Tethering is the practice of sharing the internet connectivity of one device, typically a smartphone or tablet, with another device, such as a laptop or another smartphone.
Tethering allows the device with internet access to act as a modem or router to provide internet access through various connection methods like USB, USB-C, Wi-Fi, or Bluetooth.
By tethering devices, users can utilize their mobile data plan or existing internet connection on one device to establish an internet connection on another device. This expands access to the internet in situations where traditional internet connectivity is unavailable or unreliable.
You may be wondering if tethering is necessary given the prevalence of public and private mobile hotspots.
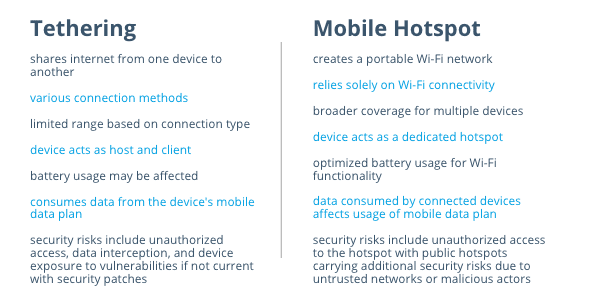
| Tethering | Mobile Hotspot |
| shares internet from one device to another | creates a portable Wi-Fi network |
| various connection methods | relies solely on Wi-Fi connectivity |
| limited range based on connection type | broader coverage for multiple devices |
| device acts as host and client | device acts as a dedicated hotspot |
| battery usage may be affected | optimized battery usage for Wi-Fi functionality |
| consumes data from the device’s mobile data plan | data consumed by connected devices affects usage of mobile data plan |
| security risks include unauthorized access, data interception, and device exposure to vulnerabilities if not current with security patches | security risks include unauthorized access to the hotspot with public hotspots carrying additional security risks due to untrusted networks or malicious actors |
As with any network connected endpoint, it is critical to implement appropriate security measures. Address employee use of tethering or mobile hotspots. Outline the steps to take when using these protocols to protect sensitive data as part of your organization’s BYOD policy.
 When is Tethering Useful in a Work Environment?
When is Tethering Useful in a Work Environment?
Employees may find themselves in areas with limited or no Wi-Fi coverage. Tethering allows them to utilize their mobile data connection and establish a reliable internet connection. This gives them access to company data, applications and computing resources or the ability to collaborate with colleagues or customers.
If your business often has people working in the field or where most of the work is performed off-site, traditional internet connectivity may not always be readily available. Having a tethering option provides your workforce with the means to establish a secure internet connection using their mobile device. This means they always have access to critical resources or real-time updates.
Tethering can play a role in other scenarios as well. Business travel, temporary offices, trade shows, conferences, or client visits are all legitimate uses for tethering to maintain uninterrupted network access to maintain productivity on the go.
In the event of a network outage or service disruption, tethering can serve as a backup internet connection. By using their personal devices and tethering capabilities, employees can maintain productivity and access essential applications while the primary network is being restored.
 Tethering, Security Risks, and Potential Cost Mitigation
Tethering, Security Risks, and Potential Cost Mitigation
Tethering is convenient, but it’s essential to address the network security risks the practice poses to your company’s sensitive data. Primary risks are unauthorized access, man-in-the-middle attacks, and data interception.
To mitigate risk, companies should establish clear guidelines to include requirements for establishing secure connections.
Policies should address:
- password protection on tethered connections
- using more robust encryption protocols such as WPA2 for Wi-Fi tethering
- restrict access to sensitive data while tethering
- requirements to keep devices updated with the latest security patches.
Since tethering consumes data from the employee’s mobile data plan, it can lead to exceeding plan limits and additional charges – a potential source of friction.
Be proactive. Consider developing guidelines on monitoring data usage to optimize consumption. If it is right for your organization, you might offer reasonable reimbursement for work-related data charges incurred from tethering in an approved use case.
In Conclusion
Embracing tethering gives you the flexibility to provide a productive work environment in and out of the office. By understanding the security risks, addressing compliance, and recognizing scenarios where tethering is needed, you can reap the benefits of tethering while safeguarding sensitive data and network security.
A tethering policy should outline acceptable use guidelines and emphasize the protection of sensitive company information. By addressing tethering in your BYOD policy, you can set clear expectations and maintain compliance standards.
When you have clear guidance in place, tethering can be a valuable tool to enhance productivity and maintain connectivity wherever work takes your employees.
 We Have Experts on Staff to Answer Your Cloud Computing Questions
We Have Experts on Staff to Answer Your Cloud Computing Questions
Interested in finding out how partnering with an award-winning cloud hosting provider can help you achieve your business goals while reducing your overall technology costs?
Our trained team of cloud computing experts can help by answering all your questions about developing internal compliance standards or developing a clear, easy to understand BYOD policy.
We’ll show you how using our efficient cloud-based storage and processing solutions in your business can improve your security, productivity, and profitability.
Let us demonstrate exactly what CyberlinkASP can do for you – using your own data, applications, and workflows.
 What is Tethering?
What is Tethering? When is Tethering Useful in a Work Environment?
When is Tethering Useful in a Work Environment? Tethering, Security Risks, and Potential Cost Mitigation
Tethering, Security Risks, and Potential Cost Mitigation We Have Experts on Staff to Answer Your Cloud Computing Questions
We Have Experts on Staff to Answer Your Cloud Computing Questions